The construction industry is undergoing a profound transformation. As environmental awareness grows and technology advances, green building practices are becoming the foundation of modern architecture. Developers, architects, and engineers are now challenged to design buildings that are not only functional and visually appealing, but also energy-efficient, sustainable, and resilient.
Advancements in Metal Cladding: From ACM to Solid Aluminum
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of building envelope design, metal cladding has emerged as a versatile and aesthetically appealing choice for architects and builders. Among the various options available, aluminum composite material (ACM) and solid aluminum panels have gained prominence due to their durability, flexibility, and modern appearance. This article delves into the advancements in metal cladding, focusing on the transition from ACM to solid aluminum, and explores the implications for design, performance, and compliance with building codes.
The Evolution of Metal Cladding
Aluminum Composite Material (ACM)
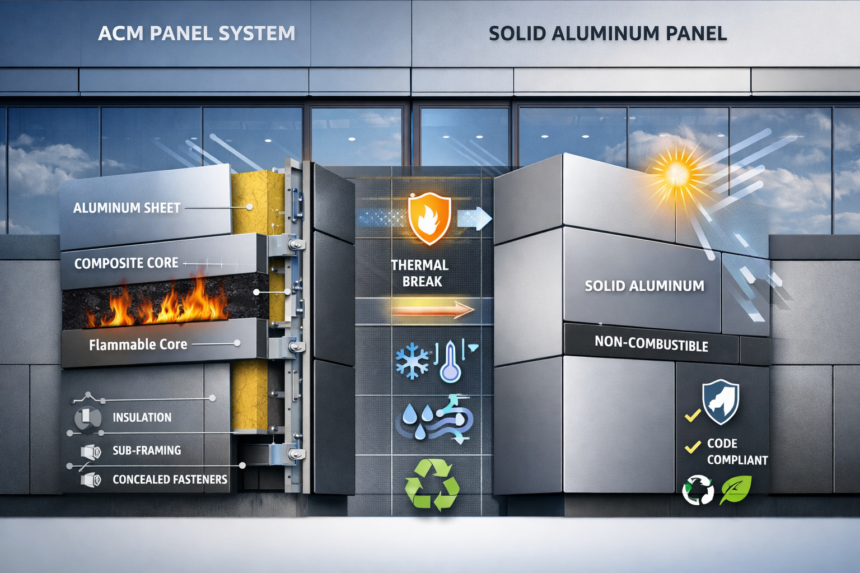
ACM panels have been a staple in modern architecture for decades. Comprising two thin layers of aluminum enclosing a non-aluminum core, ACM offers a lightweight yet robust solution for building facades. Its flexibility allows for creative design applications, making it a favorite among architects.
However, ACM has faced scrutiny due to fire safety concerns, particularly with certain core materials. This has led to increased regulatory oversight and a push for safer alternatives.
Solid Aluminum Panels
In response to these concerns, solid aluminum panels have gained traction. Unlike ACM, solid aluminum is a single-material solution, eliminating the combustible core issue. This shift addresses fire safety while maintaining the aesthetic and functional benefits of metal cladding.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Versatility in Design
Both ACM and solid aluminum offer significant design flexibility. They can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes, accommodating complex architectural visions. The range of finishes and colors available further enhances their appeal, allowing for customization to meet specific design requirements.
Aesthetic Considerations
Solid aluminum panels provide a sleek, modern look that complements contemporary architectural styles. The material’s inherent strength allows for larger panel sizes with fewer joints, contributing to a seamless appearance. This is particularly advantageous for projects aiming for a minimalist aesthetic.
Performance and Durability
Weather Resistance
Metal cladding, particularly solid aluminum, excels in weather resistance. It withstands harsh environmental conditions, including UV exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, without compromising structural integrity. This durability translates to lower maintenance costs and a longer lifespan.
Thermal Performance
While metal is a good conductor of heat, advancements in cladding systems have improved thermal performance. Insulated backing systems and strategic installation techniques can mitigate thermal bridging, enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the building envelope.
Fire Safety and Code Compliance
Addressing Fire Concerns
The transition from ACM to solid aluminum is largely driven by fire safety considerations. Solid aluminum panels do not contain combustible cores, reducing the risk of fire spread. This characteristic aligns with stricter building codes and fire safety standards implemented worldwide.
Navigating Building Codes
Compliance with building codes is paramount in the selection of cladding materials. Architects and contractors must stay informed about local regulations and ensure that the chosen materials meet or exceed these requirements. Solid aluminum panels often provide a straightforward path to compliance, given their non-combustible nature.
Practical Considerations and Common Pitfalls
Installation Challenges
While solid aluminum panels offer numerous benefits, their installation requires precision and expertise. The rigidity of the material demands careful handling to avoid damage during installation. Proper training and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential to ensure a successful application.
Cost Implications
The initial cost of solid aluminum panels can be higher than ACM. However, when considering the long-term benefits, including reduced maintenance and enhanced safety, the investment often proves worthwhile. Budgeting for these materials should account for both upfront costs and lifecycle savings.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a growing concern in the construction industry. Aluminum is a recyclable material, and choosing solid aluminum panels can contribute to a building’s overall sustainability goals. However, the energy-intensive production process of aluminum should be considered, and efforts to source recycled content can mitigate environmental impact.
Conclusion
The transition from ACM to solid aluminum panels marks a significant advancement in metal cladding technology. Offering enhanced fire safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal, solid aluminum panels are poised to become a standard in modern building envelope design. Architects, facade engineers, and contractors must weigh the benefits and challenges of these materials, ensuring compliance with evolving codes and standards. By embracing these advancements, the industry can achieve safer, more sustainable, and visually striking building envelopes that meet the demands of contemporary architecture.