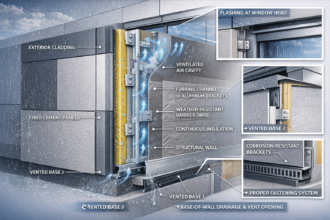
The building industry is evolving faster than ever, and material innovation lies at the heart of this transformation. As performance standards rise and sustainability becomes a global priority, engineers and manufacturers are rethinking how buildings are designed, built, and maintained.
From advanced composites to self-healing concrete, these new materials are not only improving structural integrity but also helping reduce waste, enhance efficiency, and extend the lifespan of modern buildings.
The Shift Toward Performance-Driven Materials
Traditional materials like concrete, steel, and glass remain essential, but engineering advancements are unlocking entirely new possibilities. The focus has moved from strength alone to a balance of performance, sustainability, and adaptability.
Modern materials now combine properties such as thermal insulation, lightweight strength, and recyclability creating smarter and more efficient structures capable of adapting to changing environmental conditions.
Key Innovations Transforming Building Materials
1. High-Performance Concrete
Engineers have developed new concrete formulations reinforced with fibers, nanomaterials, or polymers that increase durability and reduce cracking.
Self-healing concrete can automatically seal small fractures through chemical reactions with moisture, extending service life and cutting maintenance costs.
2. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Systems
Composite materials, such as carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), offer high tensile strength while remaining lightweight.
These materials are increasingly used in façade systems, bridge decks, and seismic retrofitting, improving both design flexibility and load performance.
3. Smart and Responsive Materials
Smart materials adjust to environmental changes in real time.
For instance, thermochromic glass tints automatically in response to sunlight, and phase-change materials absorb and release heat to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing HVAC energy consumption.
4. Sustainable Bio-Based Alternatives
Bio-based materials like mycelium bricks, bamboo composites, and hempcrete are redefining eco-friendly construction. They are renewable, naturally insulating, and significantly reduce embodied carbon while maintaining excellent durability and performance.
5. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing allows precise, waste-free production of custom components directly from digital models.
Engineers can now fabricate entire walls, panels, or structural elements with optimized material use and minimal labor, accelerating project timelines.
How Engineering is Driving Smarter Design
Engineering advancements are reshaping how materials are tested, validated, and applied. Simulation tools and Building Information Modeling (BIM) make it possible to predict how materials will perform under different stresses before construction begins.
This integration between design and engineering ensures every component supports long-term efficiency, sustainability, and occupant comfort.
Material databases and digital twins further enhance this process, providing continuous feedback during a building’s life cycle turning performance monitoring into a proactive, data-driven science.
The Future of Building Material Innovation
The future of material engineering will blend technology, sustainability, and circular economy principles.
Expect to see the rise of recyclable alloys, carbon-negative cement, and adaptive envelopes capable of responding to weather or occupancy patterns.
As buildings become more intelligent and sustainable, materials will act as active participants rather than passive elements transforming how we define strength, durability, and performance in the built environment.